When it comes to shedding extra kilos, fad diets and extreme workouts may grab attention but it’s the science of weight loss that truly matters. At its core, weight loss is a biological process driven by caloric deficit: burning more calories than you consume. But there’s much more beneath the surface.
The science behind losing weight revolves around how your body metabolizes food, regulates hormones like insulin and leptin, and converts stored fat into usable energy. It’s not just about cutting calories, it's about understanding how macronutrients (carbs, protein, fats) interact with your metabolism.
Beyond just the scale, the science beyond weight loss also focuses on muscle retention, metabolic rate, gut health, and even the role of stress and sleep. When these elements are aligned, your body becomes more efficient at burning fat sustainably.
Understanding the science of losing weight empowers you to make smarter choices like balancing protein intake, staying hydrated, and timing your meals. This is where weight loss science meets lifestyle, helping you build habits that support long-term success instead of short-term fixes.
What are the Challenges of Weight loss?
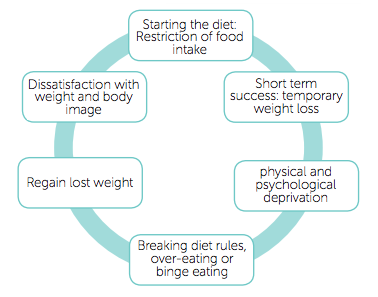
Maintaining weight loss can often be more challenging than losing the weight itself. Studies show that many individuals regain the lost weight within 2–3 years. Why? Because the effort doesn’t stop once the goal is reached. Significant weight loss typically involves major changes in diet, exercise, and lifestyle. But sustaining that progress requires long-term commitment to those habits.
The main reason for most of the diets to fail in the long run is fad diets and trendy weight-loss hacks often promise quick results, and while they might help shed a few kilos initially, the weight usually returns once you go back to your normal routine. That’s because these diets aren’t built for sustainability.
Sustainable weight loss isn’t about temporary fixes; it’s about adopting habits you can maintain for life. If your current weight loss plan involves extreme restrictions or unrealistic routines you can’t see yourself following in the long term, it’s likely the results won’t last either. (source)
Why am I not losing weight?
If you're not losing weight despite efforts to diet and exercise, then you must be missing out on these. Weight loss is a complex process influenced by numerous physiological, behavioural, and environmental factors. Here are a few possible reasons why you might not be losing weight-
1. You Might Be Eating More Than You Think
Even with a “clean” diet, hidden calories from oils, dressings, beverages, or oversized portions can prevent weight loss. Misjudging portions or forgetting to log snacks adds up fast.
Also, as you lose weight, your metabolism slows down, meaning your previous calorie intake may now be too high.
Precision in calorie tracking and using tools like food journals or apps can prevent unintentional overeating and maintain the necessary calorie deficit. (source)
According to the science behind weight loss, precision in tracking both diet and exercise is essential to avoid unknowingly sabotaging your progress.
Know how these foods will help you in your weight loss journey
2. Lack of Consistency
According to the science of weight loss, consistent habits are more effective than short-term intensity.
Occasional cheat meals, missed workouts, or weekend binges can undo the calorie deficit you’ve built during the week.
Even small but frequent lapses in diet or exercise slow down progress. Long-term weight loss success depends on regularity in sleep, meals, and activity, not perfection. (source)
3. Plateaus Are Normal
Hitting a plateau doesn’t mean your efforts have failed, it's a normal part of the science behind losing weight.
As your body adapts to weight loss, your metabolism may naturally slow down, requiring adjustments in calorie intake or activity levels.
This adaptive response is a survival mechanism, and overcoming it might involve strength training, calorie cycling, or increasing NEAT (non-exercise activity thermogenesis). (source)
4. Not Enough Physical Activity
The science of losing weight emphasizes both diet and movement. While nutrition contributes to creating a caloric deficit, physical activity accelerates fat burn and supports lean muscle growth.
Cardio helps burn calories, but resistance training boosts resting metabolic rate.
A well-rounded program combining strength training, HIIT, and everyday movement is key to activating your body’s fat-burning mechanisms. (source)
5. Not Getting Enough Sleep
Poor sleep is a silent saboteur in your weight loss journey. Lack of quality sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones like ghrelin and leptin, increasing cravings and lowering willpower.
As per modern weight loss science, sleep deprivation also reduces energy expenditure and recovery capacity. Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted sleep to support hormonal balance and metabolic function. (source)
If you feel low on sleep, or you’re turning sides all night, here is Healeo’s Melatonin+ Sleep Drops, that gives you a restful and deep sleep!
6. High Stress Levels
Stress can hinder weight loss by increasing cortisol levels in your body, which may lead to fat storage, particularly around the abdominal area.
Stress can also trigger emotional eating, which makes it difficult to maintain a caloric deficit.
Finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, yoga, or relaxation techniques, can support your weight loss goals. (source)
We know managing stress can be overwhelming, that’s why Healeo’s Ashwagandha Ultra Strength helps you calm down your stress naturally.
7. Underlying Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can make it more difficult to lose weight, even with proper diet and exercise. These include:
-
Hypothyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones, leading to a slow metabolism.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Can cause insulin resistance, which can make it harder to lose weight.
-
Insulin resistance or pre-diabetes: Can make weight loss more difficult and lead to fat accumulation.
If you suspect an underlying medical condition, consult a healthcare provider to rule out any potential issues. (source)
8. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones play a major role in regulating hunger, fat storage, and metabolism.
Leptin and ghrelin regulate feelings of hunger and fullness, while insulin helps control blood sugar. If these hormones are out of balance, it can disrupt your weight loss efforts.
Women, in particular, may experience changes in hormone levels due to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal contraceptives, which can impact weight loss. (source)
9. Gut Health and the Microbiome
Emerging research shows that the gut microbiome may play a role in weight regulation. An imbalance in gut bacteria can affect how your body absorbs nutrients and stores fat.
Incorporating probiotics and fiber-rich foods into your diet can promote a healthy gut, potentially supporting weight loss. (source)
You can also rely on probiotic supplements like Healeo's Probiotic 60 Billion CFU to boost your gut health and improve your digestive system.
10. Inconsistent Eating Patterns
Inconsistent eating habits, such as skipping meals or irregular meal timing, can affect metabolism and hunger cues.
Intermittent fasting can help some people manage their eating patterns, but for others, skipping meals may lead to overeating later in the day.
Eating regular, balanced meals can help control hunger and maintain a healthy metabolism. (source)
Factors behind Weight Loss
1. Human Metabolism
At its core, weight loss revolves around metabolism - the bodily process that converts what you eat and drink into energy. During this complex process, the calories in food and beverages combine with oxygen to release the energy needed for bodily functions.
Everyone's metabolism operates at different rates, influenced by factors such as age, sex, muscle mass, and physical activity level. Recognizing how these elements impact your metabolic rate is crucial to managing weight effectively. (source)
2. The Role of Diet in Weight Loss
Diet plays a significant role in weight loss, mainly through the balance of energy in versus energy out - a concept known as 'caloric deficit'. This involves understanding the role of macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, fats) and micronutrients (vitamins, minerals) in our diet.
Proteins help build muscle, carbohydrates provide energy, and fats support cell growth. Also, fiber and water play significant roles in maintaining satiety, thus aiding in weight loss.
Different diets impact weight loss variably, and it's important to choose a diet plan that suits individual health needs and lifestyles. (source)
Know your protein intake for weight loss!
3. The Role of Physical Activity in Weight Loss
Physical activity is another cornerstone of weight loss. Various exercises burn calories at different rates, contributing to energy expenditure.
Resistance training, for example, helps build muscle mass, which in turn increases resting metabolic rate, making weight loss easier. Including a variety of workouts in your routine can enhance weight loss and offer numerous health benefits.
4. The Psychological Aspect of Weight Loss
The mental aspect of weight loss is often overlooked. Factors such as stress and lack of sleep can affect metabolism and eating behaviors.
Additionally, maintaining motivation and discipline can be challenging, but are critical for successful, long-term weight loss. Understanding psychological barriers, such as food addiction and emotional eating, is crucial in the weight loss journey.
Understanding the Role of Genetics in Weight Loss
Genetics also play a role in body weight regulation by affecting factors such as metabolism, fat storage, and hunger. Some individuals may find it harder to lose weight due to these genetic influences.
However, the emerging field of epigenetics suggests lifestyle factors can alter how genes affect weight.
The Impact of Hormones on Weight Loss
Our body’s hormones have significant roles in weight management. Insulin, for instance, regulates blood sugar levels and promotes fat storage.
Leptin and ghrelin, known as the "hunger hormones", affect our feelings of satiety and hunger. Balancing these hormones can help maintain a healthy weight.
The Microbiome and Weight Loss
Recent research has uncovered fascinating links between our gut bacteria, known as the microbiome, and weight loss.
Different strains of bacteria play roles in metabolism and can influence weight by determining how we absorb calories and nutrients from our food.
Probiotics can potentially influence weight loss by promoting a healthier gut microbiome.(source)
How to Break Through and Start Losing Weight?
After knowing why you are not losing weight, you must be wondering and eager to know what you can do to get out of these vicious weight losing patterns, so here are a few simple and practical tips you can follow to start losing weight-
-
Track your calories: Use a food journal or app to track what you're eating and ensure you're in a caloric deficit.
-
Increase physical activity: Add more intense workouts or increase your activity level through daily steps and resistance training.
-
Prioritize sleep and stress management: Ensure you're getting enough rest and managing stress to balance your hormones.
-
Consult a healthcare provider: If you suspect a medical or hormonal issue, consult with a doctor to get personalized advice.
For an extra boost, consider using Healeo's Fat Burner Coffee, to support your weight loss journey.
Health Risks of Rapid Weight Loss and Obesity
Obesity is a serious health condition linked to numerous health problems. These include heart disease and stroke, owing to increased chances of high blood pressure and cholesterol.
Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by obesity, but can be managed or prevented through weight loss, a healthy diet, and regular physical activity.
Obesity also raises the risk for various types of cancer, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, kidney disease, and complications during pregnancy. (source)
Ready to Lose Weight? Don't Miss These 10 Weight Loss Myth Busters!
On the other hand, while weight loss can lead to improved health, losing weight too rapidly can also pose health risks.
Rapid weight loss can result in nutrient deficiencies due to reduced calorie intake, and loss of muscle mass instead of fat.
It also raises the risk of developing gallstones, severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances affecting heart rhythm, changes in blood pressure leading to dizziness and fainting, and can cause hair and skin problems due to a lack of essential nutrients.
Regardless of the circumstances, consulting with a healthcare provider is always recommended to safely and effectively manage health changes.
Read more about how much water to drink for effective weight loss
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science of weight loss extends far beyond the simple adage of 'eat less, move more'.
It involves a complex interplay of metabolism, diet, physical activity, psychology, genetics, hormones, the microbiome, and more.
Sustainable weight loss requires a comprehensive, balanced approach tailored to individual needs. As research advances, we may discover even more about the intricacies of weight loss and better strategies to promote health and wellness.
So it is best to take note of all the factors before you embark on the journey of losing weight and include a balanced healthy diet, regular exercise and Healeo's Fat Burner Coffee for visible results.
Top 10 FAQs on the Science of Weight Loss
1. What is the real science of weight loss?
The science of weight loss centers around creating a caloric deficit burning more calories than you consume. However, it also includes how hormones, metabolism, sleep, stress, and genetics interact with your body’s fat-burning ability.
Sustainable weight loss isn’t just about dieting; it's about understanding the body’s internal systems and aligning your lifestyle with long-term metabolic health.
2. Why is the science behind losing weight more complex than just cutting calories?
The science behind losing weight reveals that while calorie intake matters, so do hormonal balance, metabolic adaptation, and nutrient quality.
When you cut too many calories, your body may go into survival mode, slowing metabolism. Smart, sustainable fat loss comes from understanding how your body responds to both what and how you eat.
3. What role does metabolism play in weight loss science?
Weight loss science explains that metabolism determines how quickly your body burns energy at rest and during activity. A slower metabolism means fewer calories are burned, making weight loss harder.
Increasing lean muscle through resistance training and ensuring proper nutrition can help boost metabolic rate and improve long-term fat-burning capacity.
4. How does stress impact the science of losing weight?
Chronic stress increases cortisol, a hormone that promotes fat storage especially around the abdomen. According to the science of losing weight, stress also triggers cravings for sugary or high-fat foods, which can sabotage your progress.
Managing stress through exercise, meditation, or proper sleep helps support healthy hormone levels and weight loss efforts.
5. How do hormones affect the science of weight loss?
Hormones like insulin, ghrelin, leptin, and cortisol regulate appetite, fat storage, and energy use. When out of balance, these hormones can cause cravings, fat accumulation, or sluggish metabolism.
The science of weight loss highlights the importance of diet, sleep, and stress management to regulate these hormones and optimize fat loss.
6. What is the science beyond weight loss most people overlook?
The science beyond weight loss explores gut health, genetic predisposition, and psychological factors like emotional eating. These elements often go unnoticed but significantly impact fat loss and maintenance.
A healthy gut microbiome, positive mindset, and personalized nutrition plan can make a major difference in long-term weight management.
7. Why do people hit weight loss plateaus even after dieting?
The science behind losing weight shows that plateaus occur when your body adjusts to a lower weight, slowing metabolism to conserve energy.
To overcome this, you may need to increase strength training, change meal timing, or cycle your calories. Progress may slow but plateaus are part of the body’s natural adaptation process.
8. How important is sleep in the science of losing weight?
In weight loss science, sleep is critical. Poor sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones, reduces willpower, and increases fat-storing cortisol levels. Studies show people who sleep less tend to eat more and lose less fat.
Prioritizing 7–9 hours of quality sleep supports better hormonal regulation and weight control.
9. Can gut health influence weight loss according to science?
Yes, the science of weight loss confirms that gut bacteria affect how calories are absorbed and how fat is stored. An imbalanced microbiome may lead to inflammation, slower metabolism, and sugar cravings.
Consuming fiber-rich foods, probiotics, and fermented items supports a healthier gut and by extension improves fat loss potential.
10. Is there a difference between losing weight and fat loss in weight loss science?
Absolutely. The science of losing weight distinguishes between overall weight loss (which may include water or muscle) and fat loss.
Focusing on fat loss through strength training, adequate protein, and metabolic conditioning ensures a healthier body composition and preserves muscle mass during the weight loss process.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1498826563-db5d95e08d294ae6bc3860f901ee0c40.jpg)
